The Office of Management and Budget (OMB) revised OMB Circular A–16 in August 2002. The circular provides direction for Federal agencies that produce, maintain, or use spatial data either directly or indirectly in the fulfillment of their mission. The circular establishes a coordinated approach to electronically develop the National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI), reaffirms the Federal Geographic Data Committee (FGDC), and incorporates Executive Order 12906. The circular describes the management and reporting requirements of Federal agencies in the acquisition, maintenance, distribution, use, and preservation of spatial data by the Federal Government. Appendix E of Circular A–16 identifies 34 data themes of national significance and the responsible Federal agency. It also identifies framework data themes.
The FGDC published the Framework Introduction and Guide in 1997. This document laid the foundation concepts and requirements for the seven NSDI framework data themes. The guide identifies the NSDI as a means to assemble geographic data nationwide to serve a variety of users. The NSDI also provides an environment within which organizations and technology interact to foster activities for using, managing, and producing geographic data. The framework forms the data building blocks of the NSDI. The framework is designed to facilitate production and use of geographic data, reduce operating costs, and improve service and decisionmaking. The seven framework data themes of geographic data are those that are produced or used by most agencies and organizations, and they form a critical and useful base for the NSDI.
| Baseline (Maritime) Biological Resources *Cadastral *Cadastral (Offshore) Climate Cultural and Demographic Statistics Cultural Resources *Digital Orthoimagery Earth Cover *Elevation Bathymetric *Elevation Terrestrial Buildings and Facilities Federal Land Ownership Status Flood Hazards *Geodetic Control Geographic Names Geologic *Governmental Units |
Housing *Hydrography International Boundaries Law Enforcement Statistics Marine Boundaries Offshore Minerals Outer Continental Shelf Submerged Lands Public Health Public Land Conveyance (patent) Records Shoreline Soils *Transportation *Transportation (Marine) Vegetation Watershed Boundaries Wetlands *Indicates framework theme |
Themes in the Geospatial Line of Business
In March 2006, OMB launched the Geospatial Line of Business (LoB) as a Government-wide initiative supporting effective geospatial investments and better performance across the Federal Government. The Geospatial LoB is governed by the FGDC and focuses on improving the effectiveness of the government through more widespread use of geospatial information. The goal of the Geospatial LoB is to improve the efficiency of government by making geospatial data more accessible and reliable and less expensive to acquire through enhanced data sharing and more effective management of investments.
The Geospatial LoB is executing tasks that support Circular A–16 management and reporting requirements. These include tasks to define the stages of the geospatial data lifecycle and to define and establish Circular A–16 data steward lifecycle responsibilities, including developing a repeatable process for the evaluation and updating of the nationally significant data themes identified in Circular A–16 Appendix E. Lead agency responsibilities and new data themes may be added or altered by recommendation of the FGDC and concurrence by the OMB as stated in Appendix E.
Circular A–16 Supplemental Guidance
A draft Circular A–16 supplemental guidance package has been developed by the Geospatial LoB Lifecycle Management Work Group. The work group, which is chaired by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and has direct representation from 16 Federal agencies, used an iterative process to develop this guidance and provided extensive and repeated opportunities for interagency comment. The guidance serves as the foundation for a consistent inventory of data, clarifies and further defines the Federal geospatial framework, and provides consistent lifecycle processes to be used to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of Federal geospatial investments. When the guidance is adopted it will provide Federal agencies with a line of sight from the conceptualization of needed data, to adequate budget planning, to interagency investment decisions. It will support efforts like Imagery for the Nation (IFTN) and National Land Parcel Data.
The proposed Circular A–16 supplemental guidance establishes a repeatable process for updating the list of nationally significant data themes and their responsible lead agencies designated in Circular A–16, Appendix E. This process will better enable the FGDC to revise and add to the list in order to adapt to changes in the requirements and priorities of the Nation. For example, the current list of data themes needs to be updated to include homeland security and emergency management data themes, which have become priorities.
Status of NSDI Framework Data Themes
National Spatial Data Infrastructure (NSDI) recognizes that geospatial applications of various disciplines have a recurring need for a several themes of data—the NSDI framework. Local, regional, State, and Federal government organizations and private companies perceive the framework as a means for sharing resources, improving communication, and increasing efficiency. The framework’s seven data themes are geodetic control, digital orthoimagery, elevation, transportation, hydrography, governmental units, and cadastral information. The framework is one of the key building blocks of the NSDI and forms the NSDI’s data backbone.
Data Theme: Cadastral
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Land Management (BLM)
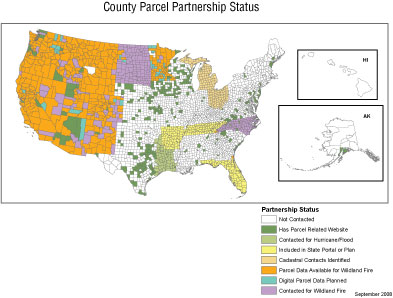
Description: In the West, the FGDC Cadastral Subcommittee contacted more than 600 counties to establish county-by-county the status and availability of parcel data to support wildfire response. In Arkansas, Florida, North Carolina, and Tennessee, State coordinators have established partnerships with the subcommittee to access parcel data. Michigan, Minnesota, and Ohio have provided contact information for county parcel data. In addition to wildfire response, Arkansas, Kentucky, Louisiana, Tennessee, and Texas have provided State coordination for county parcel data to support the response to Hurricane Ike. Additional information on the work of the subcommittee is available at www.nationalcad.org.
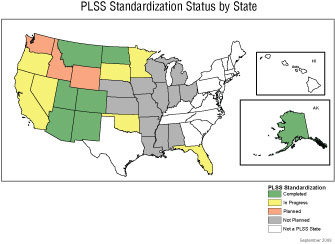
The Public Land Survey System (PLSS) is a cadastral reference system used to define many legal descriptions and other features in the 30 public domain States. Standardized PLSS representation supports geographic information system (GIS) applications that facilitate data integration, enabling searches by PLSS location. The statewide standardized PLSS representation is linked to PLSS legal survey records.
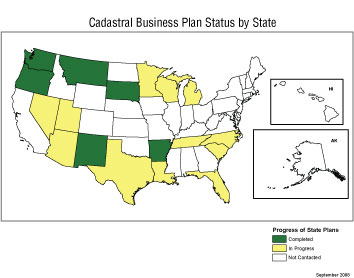
The FGDC Cadastral Subcommittee has developed a template for use in developing State business plans for cadastral information that can be developed in harmony with State strategic plans. This map shows the status of the business plans for cadastral information of those States that have been in contact with the Cadastral Subcommittee.
Data Theme: Digital Orthoimagery
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), and U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), Farm Service Agency (FSA)
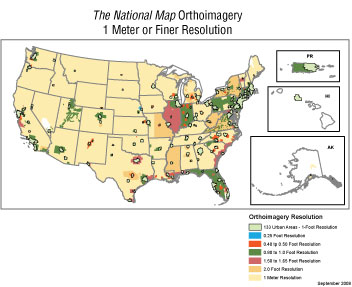
Description: The USGS is the lead Federal agency for orthoimagery; however, a number of other Federal agencies, including the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA); the FSA; the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA); the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA); the Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS); the National States Geographic Information Council; the U.S. Bureau of Land Management (BLM); and the U.S. Census Bureau, cooperate in the National Digital Orthophoto Programs (NDOP) consortium to develop and maintain national orthoimagery coverage in the public domain. The primary Federal programs for the NDOP are the NGA 133 Urban Areas Program, the USDA National Agriculture Imagery Program (NAIP), and the USGS National Orthoimagery Program.
USGS National Orthoimagery Program
The USGS National Orthoimagery Program concentrates on acquiring data in support of requirements in the following areas:
(1) High-resolution natural-color orthoimagery (1-foot
resolution) for urban areas for the Homeland Security Infrastructure
Program (HSIP), and
(2) Medium-resolution natural color orthoimagery (1-meter resolution)
in support of the National Geospatial Program’s graphic project and
maintenance of the national orthoimagery dataset.
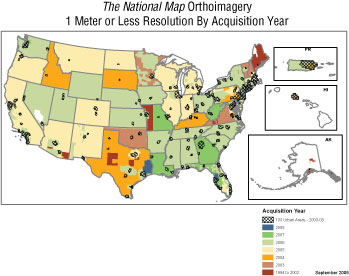
In fiscal year 2008, the Urban Areas program saved approximately $6.8 million by partnering with 27 State, regional, and city governments to acquire orthoimagery with resolutions of 1 foot or finer. Fiscal year 2008 saw the national digital orthoimagery database grow largely through partnerships for imagery at resolutions of finer than 1 meter. High-resolution (less than 2-foot resolution) orthoimagery along the Gulf Coast, mainly in Texas and Florida, was acquired to assist with emergency response. Four-band NAIP orthoimagery of 1-meter resolution covering the State of Arizona was also acquired through partnership with the FSA.
In response to FGDC Executive Committee recommendations, the USGS is coordinating with other Federal agencies on the development of plans and recommendations to implement the Imagery for the Nation (IFTN) proposal. That proposal envisions a sustainable and flexible digital orthoimagery program that meets the needs of Federal, State, Tribal, regional, and local agencies. If fully realized, the IFTN will see the creation of a national federally financed orthoimagery program that can meet the Nation’s orthoimagery needs for the future.
USDA National Agriculture Imagery Program
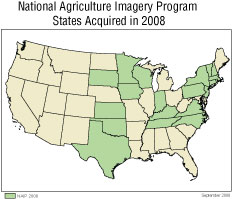
The NAIP is an annual program that acquires imagery during the growing season. FSA and other USDA agencies use the imagery to manage farm subsidy, conservation, credit and agriculture-related disaster recovery programs. In fiscal year 2008, FSA acquired imagery for 20 States, which is 6 more than in fiscal year 2007. Total acquisition cost was $14.3 million with $4.2 million coming from partnership contributions. NAIP 2008 imagery has a 1-meter ground sample distance. The imagery is in the public domain and is widely used by Federal, State and local agencies, as well as by private entities and businesses. A few examples of the business processes that the data have been used to support are economic development, emergency response, environmental management, growth planning, health and human services, homeland security, precision farming and other agribusiness activities, and transportation planning.
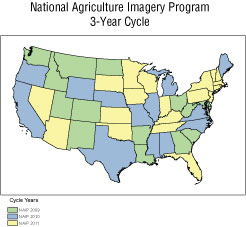
In fiscal year 2009, FSA proposes to change the NAIP significantly. Although the revised program will reduce the total amount of imagery collected each year by discontinuing the annual 2-meter-resolution collection, it will increase the frequency of collection by moving to a 3-year acquisition cycle (previously NAIP had been on a 5-year refresh cycle for 1-meter resolution). All imagery will have a 1-meter ground sample distance. The FSA will collect data on privately owned farmland as identified by common land unit boundaries and will require that other Federal and State partner participation be in place for collection outside of those areas. The partnership model for NAIP has been revised to require a minimum monetary commitment for participation. Federal agency and State government consortium partners will use the revised NAIP strategy to help plan for future funding needs and determine budget allocations.
Data Theme: Elevation
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey (USGS)
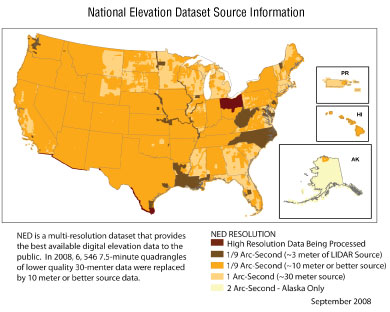
Description: The National Elevation Dataset (NED) contains elevation data that provide three-dimensional surface models of the Earth’s surface. The USGS makes elevation data available both for land areas and, in cooperation with the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), under coastal waters. The USGS identifies digital elevation data based upon the resolution (spacing between the points) of a grid. One-arc-second-resolution (equivalent to 30-meter-resolution) elevation data are complete and available for the entire United States, except Alaska. Current USGS efforts concentrate on providing finer resolution of elevation data at 1/3- and 1/9-arc-second (equivalent to 10- and 3-meter resolutions, respectively) grid spacing. The data are developed from a variety of sources, including State and local governments and the private sector.
In 2008, the trend toward higher resolution elevation data from lidar continues. Almost all new acquisitions for NED are from lidar-source products. Approximately $1 million from the USGS was leveraged to acquire $5.4 million worth of lidar data in cooperation with 32 partners, including the National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA). The NGA, working with USGS geospatial liaisons, began collaborations with State and local governments for high-resolution urban-area lidar data. Lidar data were collected along the U.S.–Mexico border, over most of Louisiana, and along the coasts of Florida and Alabama. The USGS is currently incorporating those data in the 1/9-arc-second layer of the NED, and those data will also be used to update the 1/3- and 1-arc-second data layers.
Elevation data in Alaska were reprocessed. Now all the data in NED are on the North American Datum of 1983. For the first time, portions of Alaska will be available at resolutions of 1 and 1/3 arc-seconds; the entire State will remain available at 2 arc-seconds. Radar-derived elevation data were obtained to update areas of Alaska. The inclusion of Shuttle Radar Topography Mission data in the Aleutian chain is particularly significant, as it allows the USGS to retire older data of generally poor quality.
Data Theme: Geodetic Control
Responsible agency: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), National Geodetic Survey (NGS)
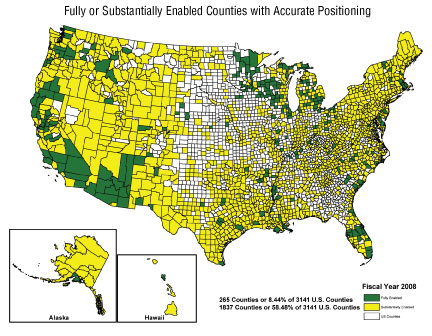
Description: The NGS is using a county scorecard to gather input from the surveying community on how better to meet local needs for accurate positioning. County usage statistics for the Online Positioning User Service (OPUS) are used as a proxy for determining positioning product usage and substantially enabled status with accurate positioning capacity. In addition, county feedback from a web-based county scorecard is a major factor in determining fully enabled status. Other factors used in the scorecard include an identified county geospatial representative, coverage by the NOAA State Geodetic Advisor program, and publication of new geodetic control stations in the NGS database. In 2008, the NGS launched a website that provided access to the information and results gathered through this scorecard initiative. The NGS has received feedback from more than 745 county geospatial representatives. Additional information is available at www.ngs.noaa.gov/scorecard/.
In the status map below, the number of U.S. counties that are substantially enabled for accurate positioning are shown in yellow; those that are fully enabled for accurate positioning are shown in green.
Data Theme: Hydrography
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey (USGS)
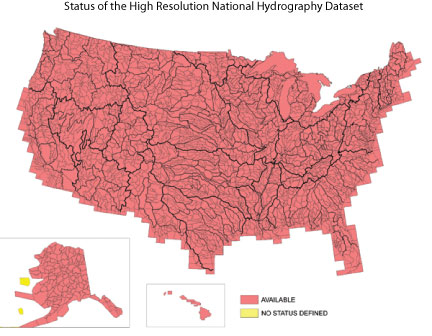
Description: These data make up the National Hydrography Dataset (NHD), which is a common data model that contains nationwide coverage of surface water features at 1:100,000 scale and 1:24,000 scale. These data have been produced by a consortium of more than 50 government agencies at the Federal and State levels to provide a universal solution for hydrography across the Nation. The USGS provides the central database, technical development, distribution, data integration, leadership, program management, coordination, and continuous maintenance through stewardship partnerships with the user community.
Data Theme: Transportation
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT), Bureau of Transportation Statistics (BTS)
Description: The DOT maintains geospatial transportation data in multiple datasets that correspond to forms of transportation. Each modal administration within the DOT may be in charge of collecting and maintaining data for one or more transportation geospatial databases related to its mode of transportation. These data collection efforts are packaged into a single transportation data resource called the National Transportation Atlas Database (NTAD). The current release of the NTAD can be found online at www.bts.gov/programs/geographic_information_services/.
The National Transportation Atlas Database is a set of nationwide geographic databases of transportation facilities, transportation networks, and associated infrastructure. These datasets include spatial information for transportation modal networks and intermodal terminals, as well as the related attribute information for these features. Metadata documentation, as prescribed by the FGDC, is also provided for each database. The data support research, analysis, and decisionmaking across all modes of transportation.
In 2008, nine transportation databases were either created or updated. These databases are Airports, Alternative Fueling Facilities, Amtrak Stations, Freight Analysis Framework, Metropolitan Planning Organization, National Bridge Inventory, Railroad Grade Crossings, Railway Network, and Waterways.
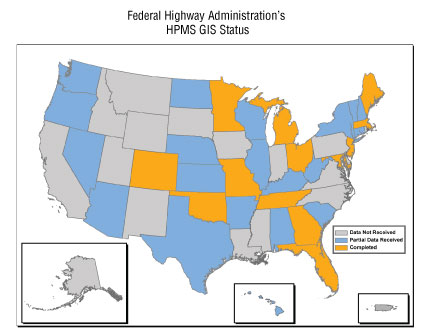
The DOT is moving ahead on several fronts to better geo-enable its data and processes. The Highway Performance Monitoring System (HPMS) is a database maintained by the Federal Highway Administration (FHWA) that depicts the condition and use of the Nation’s highway system. HPMS is a collection of highway data that FHWA collects from the States each year; it has been a significant resource to the transportation community and forms the basis for such reports to Congress as the Status of the Nation’s Highways, Bridges, and Transit: Conditions and Performance report. The HPMS database was started in the late 1970s as a tabular dataset. Today, the FHWA is in the process of linking this information to geography to allow for more robust spatial analysis and is improving the collection of data from its State partners. The map below shows the progress FHWA has made in collecting data from the States that will allow HPMS to be georeferenced to a national highway network. This project is scheduled to be completed in the spring of 2009.
The NSDI recognizes that Federal agencies have a stewardship role for certain themes of data beyond the framework themes. This year, the themes featured in this report are soils, watershed boundaries, and wetlands. A status graphic of a U.S. Census improvement project is also included.
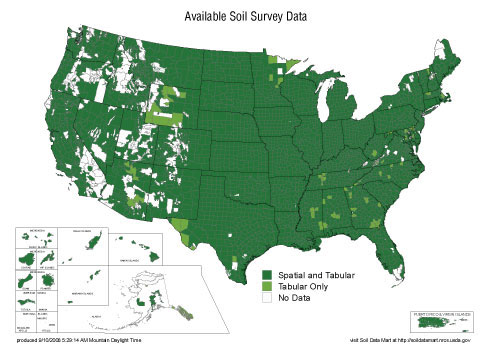
Data Theme: Soils
Responsible agency: U.S Department of Agriculture (USDA), Natural Resources Conservation Service Soil Survey Division
Description: The National Cooperative Soil Survey (NCSS) is a nationwide partnership of Federal, State, regional, and local agencies, and private entities and institutions. This partnership works together to cooperatively investigate, inventory, document, classify, interpret, disseminate, and publish information about soils of the United States and its trust territories and commonwealths.
During fiscal year 2008, NCSS created 38.9 million acres of Soil Survey Geographic Database (SSURGO) data, as well as 66 new soil survey publications and approximately 35.2 million acres of initial and updated soil survey mapping. This status map shows where detailed digital maps and associated attribute data are available. In some areas, only attribute tables are available and, in others, no soil surveys have been completed.
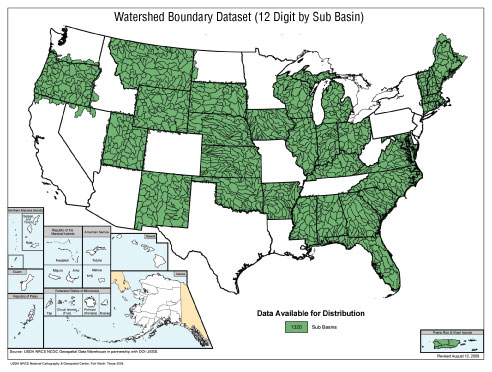
Data Theme: Watershed Boundaries
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), and U.S. Department of Agriculture, Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS)
Description: The National Watershed Boundary Dataset (WBD) is a nationally consistent, seamless, dataset that provides a consistent framework for programmatic planning, implementation, and reporting at the national, regional, and local levels. It is defined by topographic and hydrologic criteria that delineate an area of land upstream from a specific point on a river, stream, or similar surface waters. The WBD consists of a series of nested multi-level, hierarchical drainage systems.
The WBD is also used for multiple analytical and statistical purposes and applications across Federal, State, and local governments as well as non-governmental organizations. These uses include: watershed management, water-quality initiatives, watershed modeling, resource inventory and assessment, fire assessment and management, total maximum daily load calculations of pollutants, floodplain management, non-point source management planning, wetland loss mitigation, aquatic species conservation strategies, and land use management.
Efforts to complete a 1:24,000 scale WBD to 12 digits (6th level), averaging 10,000 to 40,000 acres in size, have been ongoing since the early 1990s. This level of detail has been cooperatively determined as the necessary level required to plan, implement or report protection and restoration activities. In fiscal year 2006, the USGS, the NRCS, and the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) launched an initiative to expedite the completion of this critical dataset.
Over the last 2 years, the WBD Steering Committee and the National Technical Team jointly worked with hundreds of partners nationwide to complete the WBD. This national partnership includes six additional Federal agencies, multiple departments within all 50 States, coastal management organizations, and universities. The six Federal agencies are: the National Park Service, the National Weather Service, the U.S. Bureau of Land Management, the U.S. Bureau of Reclamation, the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, and the U.S. Forest Service.
The WBD for the 48 conterminous States and Hawaii will be complete in early fiscal year 2009 and will be made available through the NRCS Geospatial Data Gateway. Plans are in place to complete Alaska by the end of FY 2009. The project focus will migrate from a development activity to a maintenance and integration phase in late 2009. Future plans are to integrate the management WBD with the National Hydrography Dataset within a single geodatabase which will be managed by the U.S. Geological Survey.
NRCS will continue maintenance and integration in fiscal year 2009, and data services will be available via the Geospatial Data Gateway. This status graphic shows the availability of WBD as of August 12, 2008.
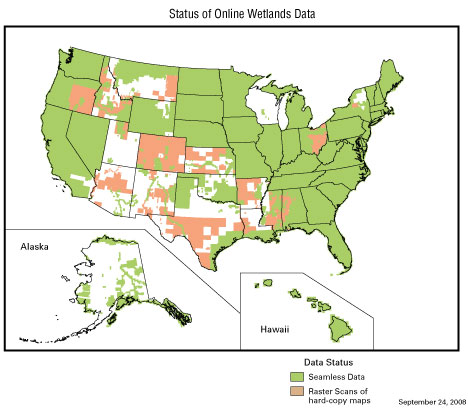
Data Theme: Wetlands
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS)
Description: Wetlands data provide the classification, location, and extent of wetlands and deepwater habitats. The FWS, in partnership with the U.S. Geological Survey, has made these data available via the Internet (wetlandsfws.er.usgs.gov). All digital wetlands data are provided in a seamless format for the conterminous United States and its territories. The FWS wetlands data are also accessible via the Geospatial One-Stop portal.
Currently, the FWS Wetlands Geodatabase contains more than 35,600 7.5-minute map areas in a seamless database. This represents wetland map data for approximately 64 percent of the conterminous United States; 29 percent of Alaska; 100 percent of the windward islands of Hawaii; 76 percent of Puerto Rico and the U.S. Virgin Islands; and 100 percent of Guam and Saipan in the Pacific Trust Territories.
Special Theme: Census Modernization
Responsible agency: U.S. Department of Commerce, U.S. Census Bureau
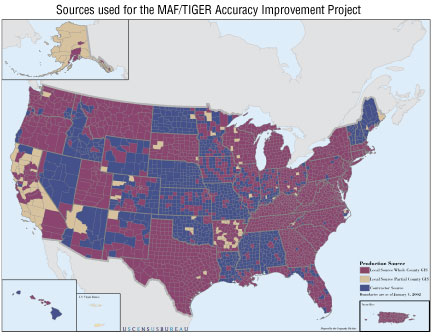
Description: The Master Address File/Topologically Integrated Geographic Encoding and Referencing (MAF/TIGER) Accuracy Improvement Project was a multiyear effort to, in part, improve the horizontal positional accuracy of the road centerlines in the U.S. Census Bureau’s nationwide seamless geospatial database, called TIGER. The MAF/TIGER database is used to support the mapping, geographic analysis, and geographic information system (GIS) activities of the Census Bureau in meeting the statistical data needs of the agency. This status map shows the sources of the data used to update the feature base of the United States, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. More than 2,000 files were obtained from Federal, State, Tribal, and local partners and used in the update process. Areas updated using local sources (whole or partial county) are indicated by the two categories called “Local Source” as shown on the status map. Areas where the contractor provided the source are now available in the public domain.
Appendix C